The word ecosystem means ecological systems. Ecology is the study of ecosystems.
An ecosystem includes all the living things (plants, animals and organisms) in a given area, interacting with each other, and with their non-living environments (weather, earth, sun, soil, climate, atmosphere). In an ecosystem, each organism has its own niche or role to play.
Ecosystems are the foundations of the Biosphere and they determine the health of the entire Earth system.
Sir Arthur George Tansley (1871 –1955) was an English botanist who introduced the concept of the ecosystem into biology.
Ernst Heinrich Philipp August (1834 –1919) was a German biologist, naturalist philosopher, physician, professor, marine biologist, and artist who discovered, described and named thousands of new species mapped a genealogical tree relating all life forms invented many words commonly used by biologists today, such as phylum, phylogeny, and ecology.
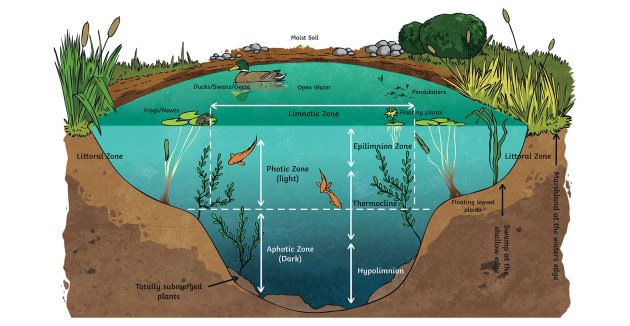
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms (plants, animals and microbes) in a particular area.
The term `eco’ refers to a part of the world and `system’ refers to the co-ordinating units. An ecosystem is a community of organisms and their physical environment interacting together. Environment involves both living organisms and the non-living physical conditions. These two are inseparable but inter-related. The living and physical components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows.
The organisms in an ecosystem are usually well balanced with each other and with their environment. An ecosystem may be natural or artificial, land-based or water-based. Artificial systems may include a cropland, a garden, a park or an aquarium. Introduction of new environmental factors or new species can have disastrous results, eventually leading to the collapse of an ecosystem and the death of many of its native species. Some of the major non-living factors of an ecosystem are: Sunlight Water Temperature Oxygen Soil Air.